In this article, We will introduce the daily ceramic production process, possible problems and solutions. After reading the post, you can control the whole manufacturing process better and fix potential problems more effectively.
The importance of daily ceramic products in life
Ceramics is one of the oldest industries, with its history dating back thousands of years. When humans discovered abundant resources of clay, mixed it with water and then fired it into objects, an important industry was born. Beginning around 9000 B.C., ceramics became popular as water and food vessels, artwork, tiles, and bricks, and their uses spread from Asia to the Middle East and Europe.
In our daily life, we are surrounded by various ceramics. From the ceramic mugs, bowls, plates and bakeware we use for dining and cooking, to the sanitary, tiles and bathroom sets for our bathrooms, and the ceramic candle jars, ornaments, vases and more we use for home decoration. Ceramic products are everywhere, adding convenience and beauty to our lives. Whether they are daily utensils or decorations, ceramic products carry people’s emotions and life memories and become an indispensable part of home life.

The daily ceramic production process and possible problems encountered
The purpose of this article is to delve into the daily ceramic production process and discuss the problems that may be encountered. By understanding the manufacturing ceramic products process, we can better understand the process and complexity of how these products are made. At the same time, we will also provide some solutions and strategies for various problems that may arise during the production process, such as cracks, glaze defects, etc., to help ceramic product manufacturers improve production efficiency and product quality, to better meet customer needs. Market demand.
Ceramics raw material preparation
Ceramic material is an inorganic, non-metallic, hard and brittle material. It is composed of several materials: mainly clays, but also feldspar (sodium, potassium or both), silica sand, iron oxides, alumina and quartz. Today’s ceramic products are rich in types. Depending on the materials used, they can be divided into traditional ceramics and specialty ceramics. Ceramics comprise numerous materials: mainly clays, additionally feldspar (sodium, potassium, or both), silica sand, iron oxides, alumina, and quartz.
- Traditional ceramics: The main raw materials of traditional ceramics are clay (AI2O3 .2SiO2 .H2O), quartz (SiO2) and feldspar (K2O·AI203·6SiO2). By adjusting the ratio of the three, different electrical resistance, heat resistance and mechanical properties can be obtained. This type of ceramic is relatively hard, but brittle, and has excellent insulation and corrosion resistance.
- Special ceramics: Special ceramics, also known as modern ceramics, include special structural ceramics and functional ceramics according to their applications, such as piezoelectric ceramics, magnetic ceramics, capacitor ceramics, high-temperature ceramics, etc. The most important high-temperature ceramics in engineering include oxide ceramics, carbide ceramics, boride ceramics and nitride ceramics.
Traditional ceramic raw materials made from clay minerals are still used today to make porcelain, clay bricks and stoneware. Specialty ceramics are used in products for medicine, aerospace, electronics and mining operations, and are even used as body armor. In this article, we will mainly talk about the raw materials of daily ceramics.
Milling
The raw materials are prepared for ceramics processing through several different techniques. This step is designed to disencumber any impurities inside the substances bearing in mind higher blending and forming, to make it extra reactive at some point of firing.
Sizing, Batching and Mixing
Through sizing, the raw materials are refined even further depending on the intended application, separating desirable materials from non-usable. Batching is part of the process also known as” blending”, which calculates amounts, weighing, and initial blending of the raw materials into predetermined compounds. Mix Ceramic powder materials in batches, usually using mixing or ball mixing methods, to obtain a more chemically and physically homogeneous material.
Mold Preparation
Ceramic molds are a crucial step in the mass production of daily ceramics. Designers will draw accurate mold design drawings based on the shape and size of the required products. These design drawings are then passed to mold makers, who use high-precision tools and techniques to create the molds, ensuring that the final ceramic product perfectly replicates the mold’s shape and texture. Molds are usually made of refractory materials such as gypsum to withstand high-temperature firing environments. Once the molds are manufactured, they will become a key tool for mass production of ceramic products, so the quality of the molds will directly affect the quality of the ceramic products.
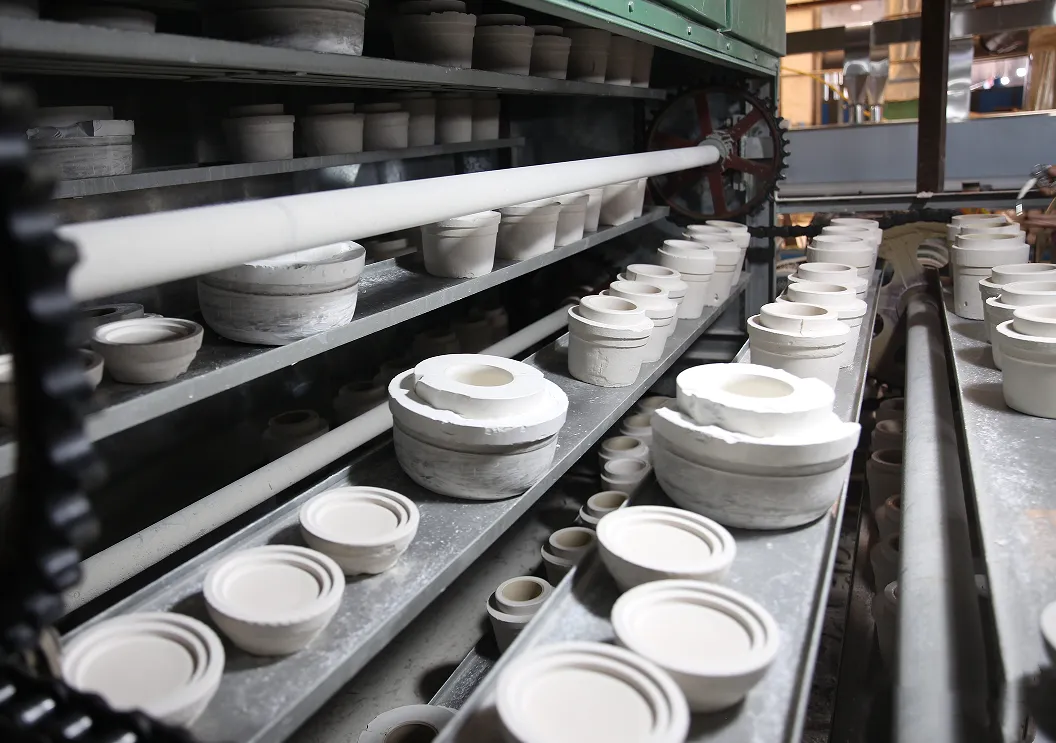

Forming Embryos
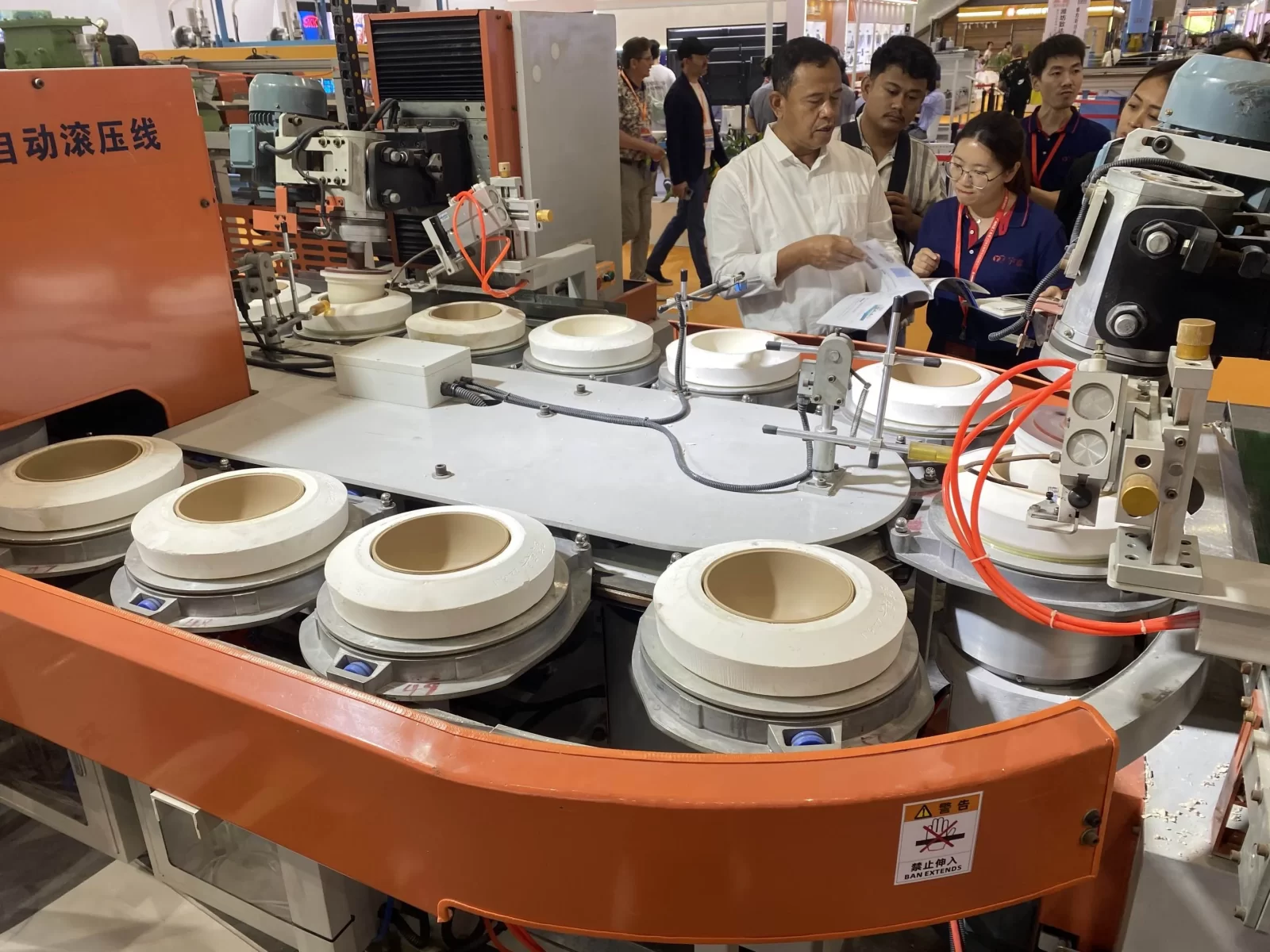
The forming of ceramic embryos is the initial stage of making ceramic products, which determines the shape and structure of the final product. In the mass production process of daily ceramics, mechanical molding is mainly used. Advanced equipment and automation technology are used to accurately inject ceramic materials into pre-designed molds to quickly and accurately form ceramic embryos. Slip molding, roll molding, and high-pressure molding are the three main technologies for ceramic raw material forming.
Drying Embryos
The drying of ceramic embryos is a crucial step in the production process, which directly affects the quality and stability of the final product. After the ceramic embryo is formed, it needs to go through a proper drying process to remove moisture and bring it to a state suitable for firing. This process is usually divided into two methods: natural drying and artificial drying. In natural drying, the ceramic embryo is placed in a well-ventilated environment, allowing natural air flow to help the water gradually evaporate. In artificial drying, drying equipment or ovens are used to controllably heat the ceramic embryo to accelerate the evaporation process of moisture. No matter which method is used, the drying process needs to be carried out carefully to avoid drying too fast or too slow, which may lead to problems such as cracking or deformation of the ceramic embryo.
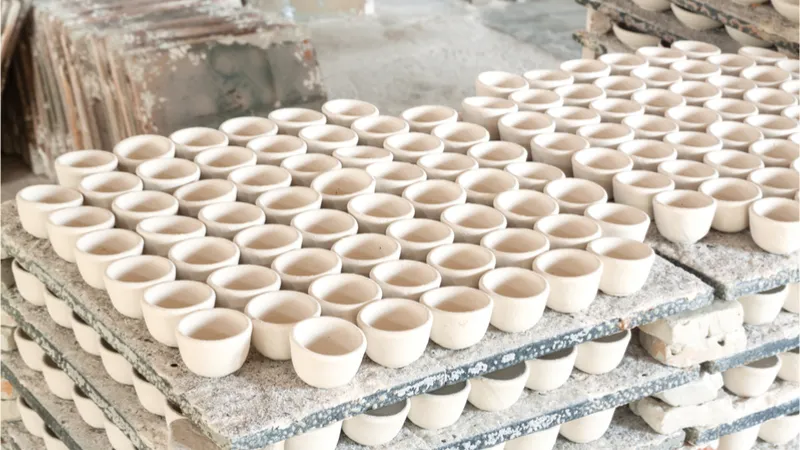

Inspection and Glazing
After forming and drying, we need to inspect the ceramic embryos’ appearance and then glaze them. Glazing is the process of soaking or spraying water on the ceramic embryos. The main purpose of this step is to allow the ceramic embryos to absorb enough moisture and shrink more evenly during the firing process, thereby reducing cracks and deformation problems during the firing process. At the same time, adding water also helps to improve the flexibility and plasticity of the embryos, making them easier to shape and process.
Firing Embryos
The firing process is a core step in the ceramic-making process, transforming the dried ceramic embryo into a strong and durable finished product. This process is usually completed in a kiln, where the ceramic embryo is sintered by high-temperature heating. Control of firing temperature and time is crucial to the quality of the final product. In the early stages of firing, the temperature is gradually increased to gradually remove residual moisture and organic matter from the ceramic, a process called the drying stage. Next comes the sintering stage. When the temperature reaches a certain level, the bonding force between ceramic particles increases, and the embryonic body begins to gradually shrink and become hard. This is followed by the firing stage, where the temperature increases further and a crystalline phase gradually forms in the ceramic embryo, giving it higher density and strength. The last step is the cooling stage, where the ceramic products are cooled to room temperature in a high-temperature environment to complete the entire firing process. Precise control and operating techniques of the firing process are crucial to ensuring the quality and performance of ceramic products.
Glazing
Glazing is a key step after embryo body firing. Covering the ceramic surface with a layer of glaze, can not only increase its gloss and beauty but also improve the wear resistance and stain resistance of the product. Glaze selection and application technique determine the texture and appearance of the final ceramic product.
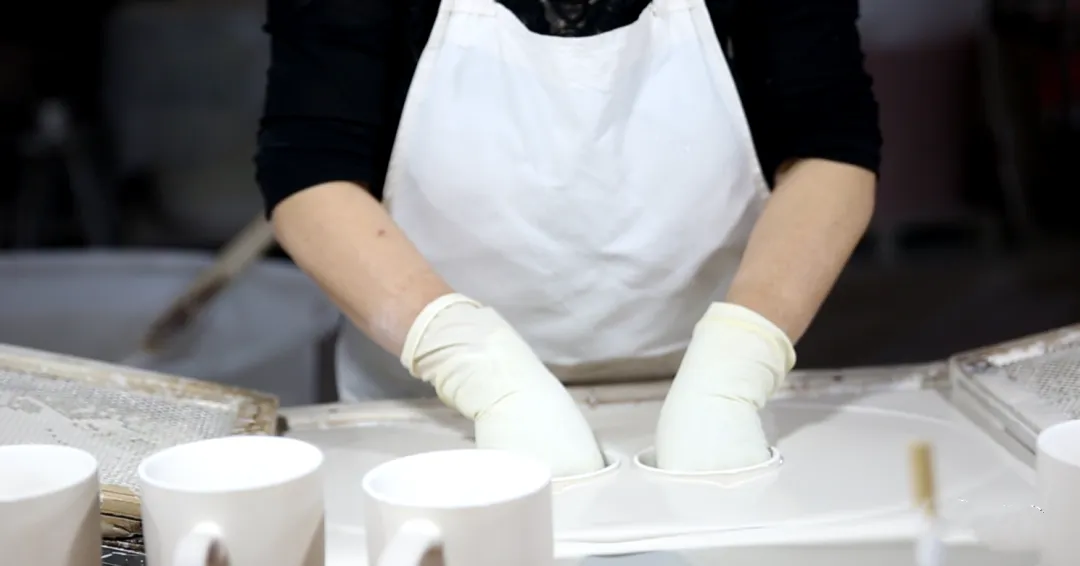

Glaze Firing
The main purpose of glaze firing is to melt the glaze applied on the ceramic surface at a high temperature to form a hard, smooth and transparent glaze. The temperature of glaze firing is usually higher than that of embryo body firing, allowing the glaze to completely melt and fuse with the ceramic body to form a dense glaze layer.
Ceramics Decoration
After the ceramic product has been glazed and fired, the selection and application of decoration become the focus of attention.
- Hand drawn: Hand-painting is a common decorative technique in which various patterns, patterns, or images are painted directly on the glaze by the artist’s hand. The advantage of hand-painting lies in its flexibility and creativity. Various unique designs can be customized according to needs, so that ceramic products present colorful visual effects, increasing their artistic value and ornamental value.
- Gold tracing: Gold tracing uses metal or gold decorative materials to draw exquisite patterns or lines on the ceramic surface. The decorative effect of gold tracing is durable and not easy to fade. It is often used for decoration and embellishment of high-end ceramic products.
- Decals: Decal is a simple and common way of decorating by attaching pre-printed patterns or images to the ceramic surface to give it a rich variety of patterns and colors. The advantages of decals lie in their low cost, simple construction, and diversified patterns. They can quickly achieve mass production and personalized customization needs.
Final Firing and Inspection
Under high temperatures, the decorative layer and the base material will fuse to form one body, while the pigments and glazes on the surface will be melted to present brilliant colors and luster. Then, the ceramic products are cooled, and after their temperature drops to a safe level, they are visually inspected to ensure quality stability and durability.
Problems May Occur During the manufacturing process
During the daily ceramic manufacturing process, various problems can arise. In this part, we will talk about 3 main issues and offer you a few solutions.
Deformation
The deformation of the ceramic product is the most common and serious defect in ceramic manufacturing. During the forming, drying, or firing process of ceramics, due to uneven temperature or pressure, the shape of ceramic products may be deformed, affecting the appearance and use of the final product.
Measure:
- Ensure the use of uniform pressure and temperature control equipment to avoid uneven forces on the ceramic during shaping, drying or firing.
-Optimize the mold design to ensure that the ceramic embryo can maintain a stable shape during the molding process.
-Adopt appropriate material formulas to improve the stability and resistance to deformation of ceramics.
Cracking
During the firing process of ceramics, due to excessive internal stress or uneven temperature changes, ceramic products may crack or break, reducing the integrity and durability of the product.
Measure:
Control the temperature and heating rate during the firing process to avoid excessive internal stress in the ceramic caused by excessive or uneven heating.
Optimize kiln equipment to ensure uniform temperature distribution and reduce the impact of thermal stress on ceramic products.
Take appropriate cooling measures during the firing process to help ceramic products gradually cool down and reduce the risk of cracking caused by thermal stress.
Foaming
During the glaze coating or firing process, if the glaze contains gas or is not evenly coated during coating, bubbles may appear on the ceramic surface, affecting the appearance and quality of the product.
Measure:
Stir and strain the glaze thoroughly to remove air bubbles and ensure a smooth surface when applied.
Use proper coating techniques such as spraying or dipping to ensure the glaze is evenly coated on the ceramic surface.
Optimize atmosphere control during the firing process to avoid oxygen or other gases entering the kiln and reduce the possibility of bubble formation.
The occurrence of these problems may affect the quality and aesthetics of ceramic products, so strict control and management measures need to be taken during the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets design requirements and customer expectations.
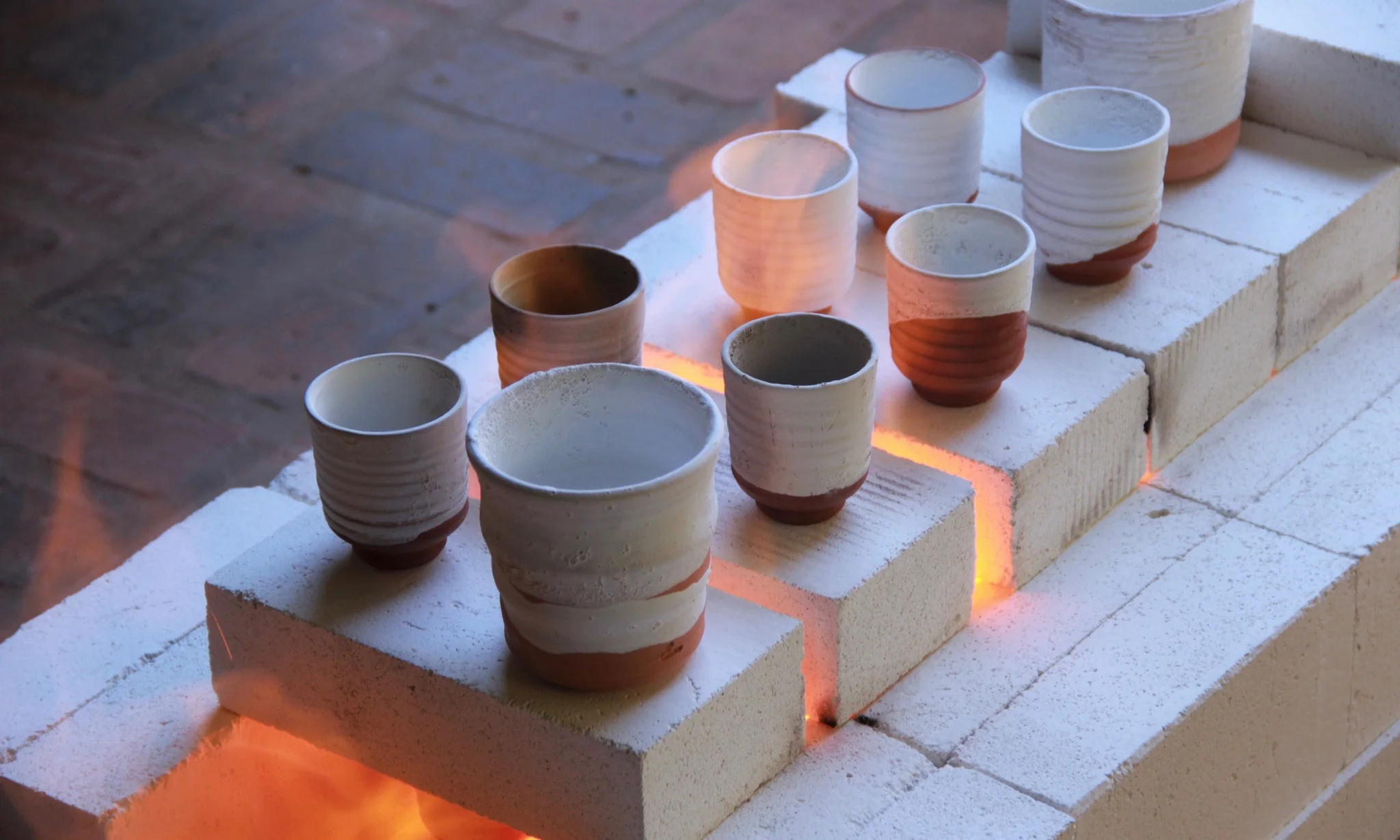

In Conclusion
While each stage in the daily ceramics manufacturing process may look different depending on the desired shape of the ceramic product and the raw materials used, the production process for these products follows a very similar process in making ceramics. model.
This article describes the complete production process from raw material preparation to final product decorative inspection for ceramic manufacturers in the Chaozhou Ceramic Manufacturers Association and provides prevention and solution strategies for common production problems such as deformation, cracking and blistering. The text provides valuable technical guidance for ceramic manufacturers to improve product quality and productivity and is an important resource for optimizing production processes and ensuring that products meet design requirements and customer expectations.
Learn more about the production process of a daily ceramics manufacturer!